Bitcoin Hashrate Falls 10% Amid Possible Xinjiang Mining Shutdowns in China
BTC/USDT
$23,298,561,101.23
$66,025.52 / $63,030.00
Change: $2,995.52 (4.75%)
-0.0012%
Shorts pay
Contents
Bitcoin’s hashrate experienced a 10% drop on Sunday due to approximately 400,000 mining rigs shutting down in China’s Xinjiang region, as stated by former Canaan co-chair Jianping Kong. This led to a loss of around 100 TH/s, highlighting vulnerabilities in global mining distribution.
-
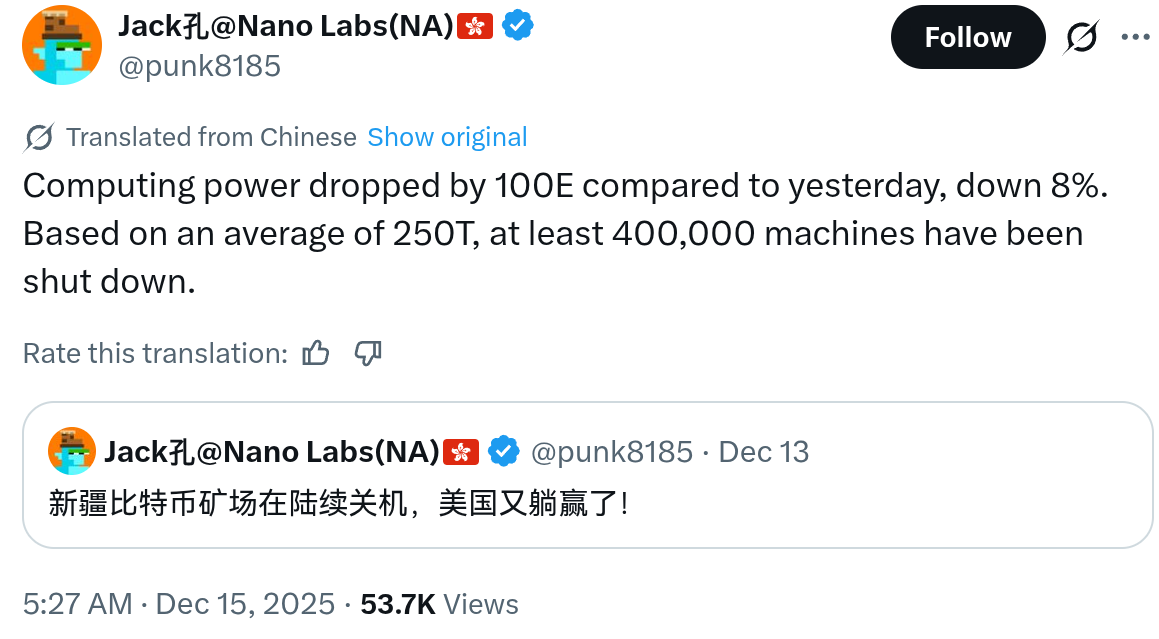
Hashrate Decline: Bitcoin’s network hashrate fell from 1,053 TH/s to 943 TH/s in one day.
-
Attribution to Xinjiang: Shutdowns in this energy-rich area disrupted operations amid China’s complex mining landscape.
-
Global Impact: The event underscores shifting power dynamics, with the US gaining ground in Bitcoin mining without direct intervention.
Explore the Bitcoin hashrate drop caused by Chinese mining shutdowns. Understand implications for network security and US dominance in 2025. Stay informed on crypto trends—read more now!
What Caused the Recent Bitcoin Hashrate Drop?
Bitcoin hashrate drop occurred abruptly when the network’s computing power decreased by about 10% in a single day. Jianping Kong, former co-chairman of mining hardware firm Canaan, linked this to the shutdown of at least 400,000 ASIC miners in China’s Xinjiang region. This estimate assumes each rig contributes roughly 250 TH/s, resulting in a 100 TH/s loss and affecting overall network stability.
How Has China’s Role in Bitcoin Mining Evolved?
China’s involvement in Bitcoin mining has fluctuated significantly over the years. Prior to 2021, the country dominated with around 65% of the global hashrate, fueled by low-cost energy and industrial-scale operations. However, a government crackdown that year forced many miners to relocate, drastically reducing its share.
By 2024, mining activities reemerged in various regions, including Xinjiang, known for its abundant hydropower and coal resources. Data from sources like Hashrate Index indicates China now holds about 14% of the world’s Bitcoin hashrate, while estimates from CryptoQuant place it between 15% and 20%. Despite the official ban, individual and corporate miners have persisted by leveraging cheap electricity, as reported by Reuters in late 2024.
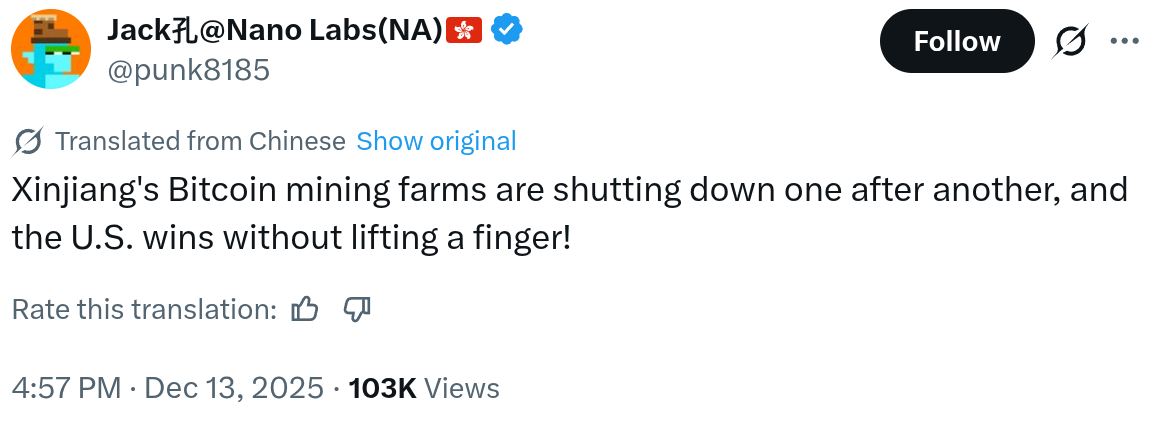
Jianping Kong expressed frustration over the Xinjiang shutdowns, noting in a recent statement that they benefit the United States “without lifting a finger.” This reflects ongoing tensions between regulatory pressures and economic incentives in China’s mining sector. Experts emphasize that such disruptions highlight the need for diversified hashrate to maintain Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, with short paragraphs aiding quick comprehension of these complex shifts.
Source: Jianping Kong
The Bitcoin hashrate drop not only impacts immediate network performance but also signals broader geopolitical influences on cryptocurrency infrastructure. YCharts data confirms the decline from 1,053 TH/s on Sunday to under 943 TH/s on Monday, equivalent to over 110 TH/s lost. While hashrate is an inferred metric based on network difficulty adjustments, this event underscores the fragility of concentrated mining regions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Bitcoin hashrate drop in Xinjiang?
The shutdown of around 400,000 mining rigs in Xinjiang represents a major disruption, reducing Bitcoin’s total hashrate by 10%. This event, tied to local energy policies or enforcement, illustrates how regional factors can swiftly alter global mining dynamics and potentially increase vulnerability to attacks during low hashrate periods.
How does China’s mining ban affect Bitcoin’s global network?
China’s ongoing mining restrictions, despite some underground operations, have redistributed hashrate worldwide, boosting regions like the US and North America. This shift enhances Bitcoin’s resilience by promoting decentralization, though it occasionally leads to temporary drops like the recent one, ensuring the network remains robust against single-point failures.
Source: Jianping Kong
In parallel, the United States is aggressively expanding its Bitcoin mining capabilities. Companies like Hut 8, which announced four new sites in Texas, Louisiana, and Illinois at the end of August—adding 1.5 gigawatts of capacity—demonstrate this momentum. As the parent of American Bitcoin, a firm connected to the Trump family, Hut 8’s public merger in early May further integrates political and financial interests in the sector.
Eric Trump serves on the board, signaling high-level endorsement. Meanwhile, scrutiny on Chinese hardware persists; late November 2024 reports highlighted a US investigation into Bitmain, the leading ASIC producer, over national security risks like remote control capabilities that could threaten the power grid. This probe follows earlier actions, including a US Customs halt on Bitmain shipments in November 2024, with releases only beginning in March 2025.
Additionally, October 2024 saw probes into Bitmain-linked firms like厦门 Sophgo for ties to sanctioned entity Huawei. American Bitcoin itself acquired 16,299 Antminer U3S21EXPH units from Bitmain, potentially facing repercussions. These developments position the US to challenge China’s historical dominance in both mining operations and hardware manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- Xinjiang Shutdown Impact: The closure of 400,000 rigs caused a 10% Bitcoin hashrate drop, emphasizing regional risks in mining.
- US Expansion: Firms like Hut 8 are scaling up with new sites, capturing more global hashrate amid China’s constraints.
- Security Scrutiny: Ongoing US investigations into Chinese ASICs highlight efforts to secure domestic infrastructure.
Conclusion
The recent Bitcoin hashrate drop in China’s Xinjiang region, as detailed by expert Jianping Kong, reveals persistent challenges in the country’s mining environment despite its historical dominance. With the US rapidly advancing through investments and regulatory measures targeting foreign hardware, the global Bitcoin mining landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. As hashrate redistributes, stakeholders should monitor these shifts to capitalize on emerging opportunities and bolster network security—positioning 2025 as a pivotal year for decentralized innovation.
Comments
Other Articles
Bitcoin Price Analysis: Will the Uptrend Continue?
2/28/2026
Ethereum 2.0 Update: How Will It Affect the Crypto Market?
2/27/2026
The Coming of Altcoin Season: Which Coins Will Stand Out?
2/26/2026
DeFi Protocols and Yield Farming Strategies
2/25/2026
