DeFi Could Save Up to $30 Billion Yearly on Remittance Costs, Per Advocacy Group
ETH/USDT
$15,764,184,570.61
$1,937.17 / $1,835.36
Change: $101.81 (5.55%)
-0.0004%
Shorts pay
Contents
DeFi technology could save up to $30 billion annually by reducing remittance costs for unbanked individuals worldwide, according to the DeFi Education Fund. This reduction, potentially up to 80%, leverages blockchain to eliminate intermediaries and lower fees on international money transfers.
-
DeFi targets high remittance fees that burden low-income workers sending money home.
-
By removing traditional intermediaries, DeFi cuts costs significantly for global transfers.
-
The DeFi Education Fund reports that 56% of American adults value full control over their finances through DeFi features.
Discover how DeFi reduces remittance costs by up to 80%, saving $30 billion yearly for the unbanked. Explore blockchain’s role in fighting poverty and enhancing financial access today.
How Does DeFi Reduce Remittance Costs?
DeFi reduces remittance costs by utilizing blockchain infrastructure to bypass traditional banking intermediaries, enabling faster and cheaper cross-border transfers. The DeFi Education Fund highlights that this approach could save unbanked and underbanked individuals around the world approximately $30 billion each year. Workers sending funds home often face exorbitant fees, but DeFi platforms streamline these processes, potentially lowering expenses by up to 80% through automated smart contracts.
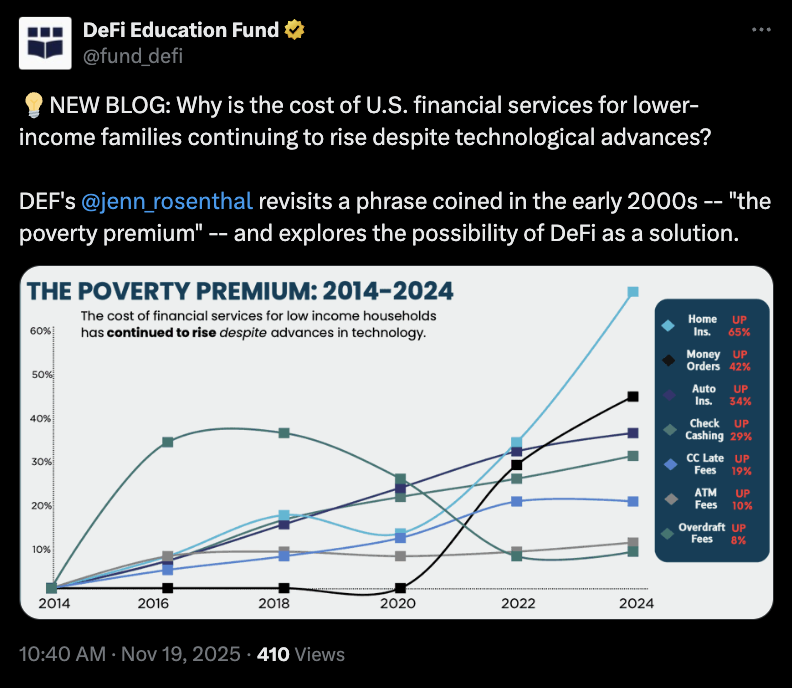
Source: DeFi Education Fund
What Is the Poverty Premium and How Does DeFi Address It?
The poverty premium refers to the extra expenses low-income households pay for basic financial services, such as cashing checks or using money orders, compared to wealthier individuals who access lower-cost options through banks. The DeFi Education Fund explains that outdated financial systems make it costly to serve low-income customers profitably, perpetuating this cycle. DeFi counters this by decentralizing services via blockchain, eliminating layers of bureaucracy and reducing fees— for instance, the fund notes that remittance costs could drop dramatically, freeing up funds for essentials. Experts from the organization emphasize that while DeFi does not make services entirely free, it leverages efficient software to provide greater control and affordability. Supporting data from the fund’s analysis shows that unbanked Americans alone face rising costs for everyday transactions, with DeFi offering a scalable alternative. This shift not only lowers immediate expenses but also builds long-term financial inclusion, as seen in global examples where blockchain has already streamlined micropayments and peer-to-peer transfers without traditional gatekeepers.
The DeFi Education Fund, an advocacy group dedicated to promoting decentralized finance, outlined these benefits in a detailed blog post released on Wednesday. Their report focuses on how DeFi can tackle poverty both in the United States and internationally by making financial tools more accessible. For many migrant workers, sending money across borders involves hefty charges from banks or wire services, but DeFi protocols use distributed ledgers to process transactions securely and at a fraction of the cost.
“The poverty premium persists because the current, layered, antiquated financial infrastructure makes it expensive to serve low-income customers profitably,” stated the DeFi Education Fund. They further elaborated: “Nothing is free, and DeFi doesn’t eliminate costs entirely, but by removing intermediaries and leveraging software rather than outdated financial systems, we can dramatically reduce the cost of financial services for everyday people and give them greater control of their finances.”
Blockchain advocates have long pushed for technology to combat poverty drivers like slow transaction times and high fees. The fund specifically points to U.S. challenges, including the expenses of cashing paychecks without a bank account, relying on money orders, or even homeownership barriers for the underbanked. By integrating DeFi, these pain points could be alleviated, allowing individuals to retain more of their earnings.
Related: DappRadar’s token price plummets after platform announces shutdown.
Public interest in DeFi remains promising despite limited familiarity. The DeFi Education Fund reports that while only 3% of Americans are very familiar with DeFi, a majority find its principles attractive. Specifically, 56% of American adults prioritize full personal control over their money at all times, 54% seek control over the security of their personal and financial data, and 53% desire constant access to their full financial history. These statistics underscore DeFi’s potential to resonate with everyday users seeking empowerment in their financial lives.
Looking for Policies and Laws Favorable to DeFi
In the United States, congressional efforts to regulate digital assets are gaining momentum, which could directly impact DeFi’s growth in reducing remittance costs. Lawmakers are advancing a comprehensive market structure bill for digital assets, with Republican versions from the Senate Agriculture and Banking Committees serving as discussion drafts. Bipartisan negotiations continue to shape the final legislation, addressing how decentralized protocols fit into broader financial regulations.
In October, Senate Democrats on the banking committee expressed concerns over the Republican drafts, proposing amendments that might impose restrictions on DeFi under certain conditions, such as enhanced oversight for consumer protection. Despite these debates, the bill’s progress persists following a 43-day government shutdown that concluded last week.
Senate Banking Chair Tim Scott has indicated optimism, expecting the legislation to be signed into law by early 2026. This framework could provide clarity for DeFi innovations, potentially accelerating their adoption for cost-saving applications like remittances. Clear policies would encourage investment in blockchain infrastructure, ensuring that technologies aimed at financial inclusion are supported rather than stifled. As the DeFi Education Fund advocates, favorable regulations are essential to unlocking the full $30 billion in annual savings potential, benefiting millions worldwide by making global money movement more equitable and efficient.
Magazine: Ethereum’s Fusaka fork explained for dummies: What the hell is PeerDAS?
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Estimated Annual Savings from DeFi in Global Remittances?
The DeFi Education Fund estimates that decentralized finance could generate up to $30 billion in annual savings by cutting remittance costs for unbanked and underbanked populations. This figure accounts for reduced fees on international transfers, which currently burden low-income workers sending money home from abroad.
How Appealing Is DeFi to Everyday Americans for Financial Control?
DeFi appeals strongly to many Americans who value personal autonomy in finance. According to the DeFi Education Fund, 56% appreciate full control over their money anytime, 54% prioritize data security, and 53% want easy access to their financial history, making it a natural fit for modern needs.
Key Takeaways
- DeFi’s Cost-Cutting Power: Blockchain eliminates intermediaries, potentially reducing remittance fees by up to 80% and saving $30 billion yearly for global users.
- Combating the Poverty Premium: Outdated systems charge low-income households more; DeFi provides affordable alternatives like cheaper check cashing and transfers.
- Growing Public Interest: With over half of Americans favoring DeFi’s control features, adoption could surge if supportive policies emerge by 2026.
Conclusion
In summary, DeFi reduces remittance costs by harnessing blockchain to deliver efficient, low-fee financial services, as evidenced by the DeFi Education Fund’s projection of $30 billion in annual global savings. Addressing the poverty premium through decentralized protocols not only empowers the unbanked but also aligns with public demands for greater financial control. As U.S. lawmakers finalize digital asset regulations by early 2026, the path for DeFi’s expansion looks promising—urging stakeholders to invest in this transformative technology for a more inclusive financial future.
Comments
Other Articles
Bitcoin Price Analysis: Will the Uptrend Continue?
3/1/2026
Ethereum 2.0 Update: How Will It Affect the Crypto Market?
2/28/2026
The Coming of Altcoin Season: Which Coins Will Stand Out?
2/27/2026
DeFi Protocols and Yield Farming Strategies
2/26/2026
