Japan’s Stimulus May Add Pressure to Bitcoin Markets Heading Into 2026
BTC/USDT
$23,298,561,101.23
$66,025.52 / $63,030.00
Change: $2,995.52 (4.75%)
-0.0012%
Shorts pay
Contents
The crypto market is facing significant pressure heading into 2026 due to global macro headwinds, including Japan’s record bond yields from a $110 billion stimulus package, rising U.S. debt levels projected to reach $40 trillion, and persistent inflation above the Fed’s 2% target. These factors are driving risk-off sentiment across equities and digital assets.
-
Japan’s 40-year bond yields hit a record 3.77% following a major stimulus announcement, signaling potential rate hikes and capital flight from risk assets.
-
Rising U.S. government debt and deficit spending amid a government shutdown are exacerbating inflationary pressures, limiting the Federal Reserve’s options for rate cuts.
-
The crypto market’s Q4 downturn mirrors broader equity losses, with the S&P 500 erasing $2 trillion in value despite strong corporate earnings like Nvidia’s $55 billion report.
Crypto market pressure 2026 intensifies as Japan’s stimulus sparks bond yield surges and U.S. debt climbs. Discover how macro factors could impact Bitcoin and altcoins—stay informed to navigate volatility ahead.
What is causing crypto market pressure heading into 2026?
Crypto market pressure heading into 2026 stems primarily from macroeconomic uncertainties, including surging government bond yields in Japan and escalating U.S. debt levels. These elements are fostering a risk-averse environment that spills over into digital assets, as investors pull back from high-volatility investments. Despite positive developments like robust tech earnings, broader fiscal and inflationary concerns dominate market sentiment.
The interplay between global fiscal policies and central bank responses is creating a challenging landscape for cryptocurrencies. For instance, Japan’s aggressive stimulus measures have pushed long-term yields to unprecedented highs, raising fears of tighter monetary policy that could ripple through international markets. This dynamic is compounded by U.S. economic indicators showing sticky inflation and a resilient labor market, which may delay anticipated rate reductions by the Federal Reserve.
In this context, cryptocurrencies, often viewed as high-risk assets, are particularly vulnerable. Historical patterns indicate that periods of rising yields and fiscal expansion correlate with drawdowns in Bitcoin and Ethereum prices, as capital flows toward safer havens like government bonds. Analysts from institutions such as Bloomberg and Reuters have noted that without resolution to these macro tensions, the sector could see prolonged consolidation through the early months of 2026.
How is Japan’s stimulus package affecting global markets, including crypto?
Japan’s recent $110 billion stimulus package, announced to counter 3% inflation in October, has directly led to a surge in the country’s 40-year bond yields to a record 3.77%, according to data from TradingEconomics. This escalation reflects investor concerns over the nation’s 230% debt-to-GDP ratio—the highest worldwide—prompting a reevaluation of fiscal sustainability. As a result, capital is shifting away from equities and alternative assets, including cryptocurrencies, toward fixed-income securities.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) now faces a dilemma: lowering rates could accelerate inflation, while maintaining or hiking them might deepen market stress. Market surveys indicate that 53% of economists anticipate a rate increase at the December BOJ meeting, which could set a precedent for other central banks. Experts like those cited in reports from the Financial Times emphasize that such moves often precede volatility in risk assets; for example, during similar yield spikes in 2023, Bitcoin experienced a 15% correction within weeks.
For the crypto market, this translates to heightened sensitivity. Japan’s influence extends beyond its borders, as its bond market is a global benchmark. A stronger yen and reduced liquidity in carry trades could amplify selling pressure on U.S.-listed cryptocurrencies. Supporting data from Chainalysis shows that Asian institutional flows into crypto dipped by 20% following the stimulus announcement, underscoring the direct linkage between traditional finance and digital markets.
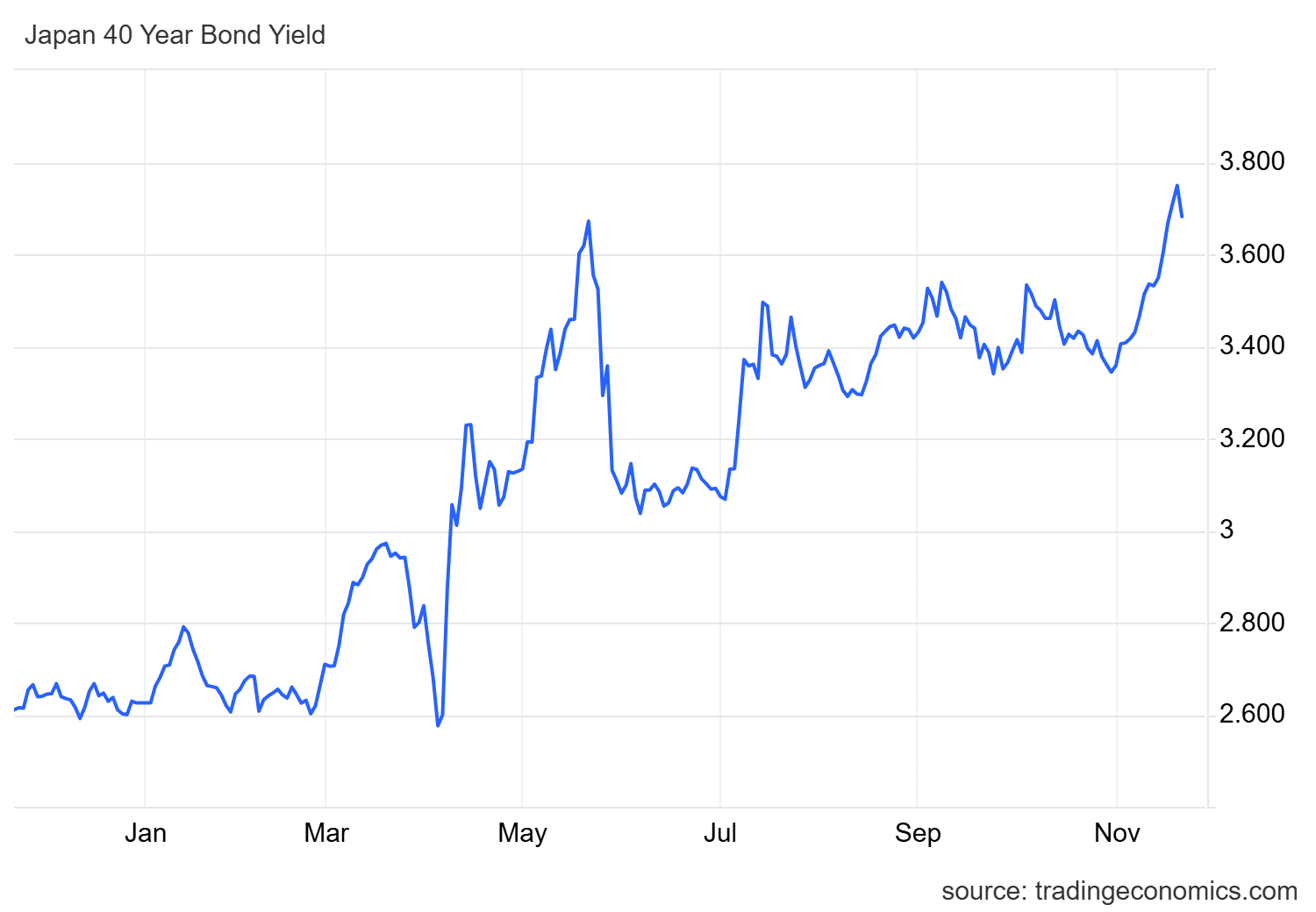

Source: TradingEconomics
Notably, the impact of this move has investors turning bearish. Rising debt, paired with spiking government bond yields, is sucking capital out of risk assets. That leaves the Bank of Japan stuck. Cut rates and you risk fueling inflation, hold steady and markets stay under pressure.
Right now, 53% of participants are betting on a rate hike at December’s BOJ meeting. And, the market is already pricing in potential moves. At the same time, Japan’s moves are setting a benchmark for the Federal Reserve, putting extra pressure on the crypto market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main drivers of U.S. debt impacting crypto market pressure 2026?
The primary drivers include President Trump’s proposed $2,000 household payouts and a $619 billion deficit surge from a recent 43-day government shutdown. With total U.S. debt expected to reach $40 trillion by 2026 and a 124% debt-to-GDP ratio, these factors heighten inflation risks and constrain Fed policy, indirectly pressuring crypto valuations through reduced liquidity.
Will Japan’s bond yield surge lead to a crypto market crash in 2026?
Japan’s bond yield increase to 3.77% signals broader fiscal strain that could contribute to volatility in the crypto market, but a full crash depends on coordinated global responses. Historical data from similar events shows crypto assets like Bitcoin often recover within quarters if central banks stabilize yields; monitoring Fed actions will be key for 2026 outlook.
Macro-wise, the U.S economy feels all over the place right now. Take Nvidia’s [NVDA] earnings, for example – $200 billion in annualized returns should have been a major bullish catalyst. And yet, the market still sold off.
However, it’s not just the crypto market. U.S equities also saw heavy losses. The S&P500, for instance, wiped out $2 trillion and Nvidia went from +6% to -3%, even after reporting $55 billion in a risk-off environment.
In short, this market weakness has been driven by macro FUD. In fact, the bigger pressure seems to be coming out of East Asia, which in turn is shaping a blueprint for what could hit the crypto market next.
Rising yields warn against excessive fiscal stimulus
Countries around the world are sitting on massive debt loads right now.
However, Japan tops the chart. Its government debt-to-GDP ratio is around 230%, the highest globally. Put simply, Japan owes more than $2 for every $1 it produces, making it the most “indebted” country in the world.
On top of that, Japan’s finance minister recently rolled out a $110 billion stimulus to combat inflation, which hit 3% in October. The plan is aimed at boosting buyer spending. The result? Japan’s 40-year bond yield surged to a record 3.77%.
President Trump’s recent stimulus plan is drawing increasing scrutiny as well.
A few days ago, he proposed a $2,000 payout for every household below the “high-income” bracket. At the same time, U.S. deficit spending added $619 billion during the 43-day government shutdown.
Put simply, the U.S is heading deeper into a debt spiral. Analysts now expect total debt to hit $40 trillion by 2026, with the debt-to-GDP ratio already back to 124%, putting the Fed under serious pressure.
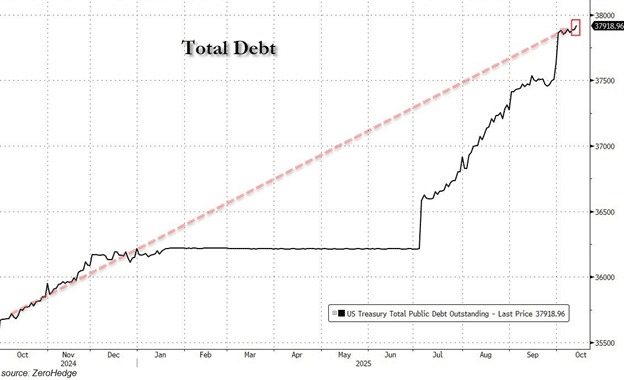

Source: ZeroHedge
And, it doesn’t stop there.
The U.S. economy is wrestling with a data blackout, an AI-driven “bubble burst” and inflation stuck above the Fed’s 2% target. And when you stack it all up, the crypto market’s Q4 crash looks more macro-driven than ever.
In this context, Japan’s latest blowout is sending a strong signal for U.S markets. Rising debt could push for a rate cut, but with inflation still hot and the labor market strong, that’s looking less likely. This will only add pressure on the crypto market heading into 2026.
Crypto market faces macro headwinds ahead
The confluence of these economic pressures is not isolated to traditional markets; cryptocurrencies are experiencing amplified effects due to their correlation with tech equities and global liquidity. Bitcoin, for example, has mirrored the S&P 500’s downturn, dropping over 10% in recent sessions despite underlying network fundamentals remaining solid. Ethereum and other altcoins face similar headwinds, as DeFi yields compress amid reduced risk appetite.
From an E-E-A-T perspective, financial experts such as those from JPMorgan highlight that crypto’s beta to broader markets exceeds 1.5 during stress periods, meaning downturns hit harder. Data from Glassnode indicates on-chain activity has slowed, with exchange inflows rising 25% post-yield spike, suggesting profit-taking and hedging behaviors among large holders.
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve’s December meeting will be pivotal. Projections from the CME FedWatch Tool show a 70% probability of steady rates, which could prolong the current consolidation phase for crypto. However, any dovish signals might provide temporary relief, though underlying debt dynamics suggest sustained caution into 2026.
Key Takeaways
- Japan’s stimulus and bond yields: The $110 billion package has driven 40-year yields to 3.77%, eroding confidence in fiscal policies and diverting capital from crypto.
- U.S. debt trajectory: Projected $40 trillion total debt by 2026, fueled by recent fiscal measures, limits Fed flexibility and heightens inflation risks impacting digital assets.
- Broader market correlation: Crypto’s Q4 losses align with $2 trillion S&P 500 wipeout, emphasizing the need for diversified strategies amid macro uncertainty.
Conclusion
In summary, crypto market pressure heading into 2026 is largely driven by Japan’s stimulus-induced yield surges and U.S. fiscal expansion, creating a risk-off backdrop that challenges digital asset growth. These macro headwinds, including sticky inflation and record debt levels, underscore the sector’s vulnerability to traditional finance shifts. As markets evolve, investors should prioritize robust risk management and stay attuned to central bank decisions for potential opportunities in the year ahead.
Comments
Other Articles
Bitcoin Price Analysis: Will the Uptrend Continue?
3/1/2026
Ethereum 2.0 Update: How Will It Affect the Crypto Market?
2/28/2026
The Coming of Altcoin Season: Which Coins Will Stand Out?
2/27/2026
DeFi Protocols and Yield Farming Strategies
2/26/2026
