Poland Veto Upholds Crypto Act Block, Slowing EU Rules as Bitcoin Adoption Grows
BTC/USDT
$23,298,561,101.23
$66,025.52 / $63,030.00
Change: $2,995.52 (4.75%)
-0.0012%
Shorts pay
Contents
Poland’s parliament failed to override President Karol Nawrocki’s veto on the Crypto-Asset Market Act, delaying EU-aligned crypto regulations and sparking debates on balancing security with innovation in the digital asset sector.
-
Parliament lacked the three-fifths majority needed to override the veto, halting the bill’s progress.
-
The act aimed to align Poland with the EU’s MiCA framework for overseeing crypto markets.
-
Despite the regulatory pause, Poland’s crypto adoption grew over 50% in transaction volume year-over-year, per Chainalysis data.
Poland’s Crypto-Asset Market Act veto delays EU crypto rules, fueling innovation vs. security debate. Discover impacts on adoption and next steps for regulation. Stay informed on Poland crypto regulation developments.
What is the Crypto-Asset Market Act in Poland?
The Crypto-Asset Market Act was a proposed legislation in Poland designed to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for digital assets, aligning the country with the European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation. Introduced by Prime Minister Donald Tusk’s government in June 2025, the bill sought to address licensing, compliance, and security measures for crypto service providers. However, President Karol Nawrocki vetoed it last week, citing risks to personal freedoms, property rights, and national stability.
The veto has significant implications for Poland’s evolving crypto landscape. Lawmakers in the lower house attempted to override it but fell short of the required three-fifths majority, effectively stalling the regulatory push. This development underscores ongoing tensions between government efforts to enhance oversight and concerns over excessive restrictions that could hinder growth in the sector.
Source: Kancelaria Prezydenta RP
Why Did President Nawrocki Veto the Crypto-Asset Market Act?
President Nawrocki vetoed the Crypto-Asset Market Act due to apprehensions that its provisions could infringe on individual liberties and economic freedoms. He argued that the bill’s stringent requirements might undermine property rights and threaten state stability, as stated in official communications from his office. Supporters of the veto, including some industry stakeholders, echoed these concerns, highlighting overly burdensome licensing processes and high compliance costs that could deter innovation.
The legislation included criminal liability for executives of crypto service providers and rigorous reporting obligations, which critics said would create an uncompetitive environment for startups. According to reports from Bloomberg, the president’s decision reflects broader divisions within Poland’s political and business communities. Proponents of the bill, however, viewed it as essential for national security, aiming to prevent fraud and mitigate risks from foreign influences, such as potential misuse by actors like Russia. Data from the European Banking Authority supports the need for such frameworks, noting that unregulated crypto markets have seen a 20% rise in illicit activities across the EU in recent years.
With the veto upheld, Poland’s government must now revisit its approach to crypto regulation. This pause could prolong uncertainty for businesses operating in the space, potentially affecting investment flows. Experts like Dr. Elena Kowalska, a financial regulation specialist at the University of Warsaw, have noted that “while security is paramount, overly rigid rules risk pushing innovation offshore, as seen in other European nations.”
How Is Crypto Adoption Progressing in Poland Amid Regulatory Delays?
Despite the regulatory setback with the Crypto-Asset Market Act, cryptocurrency adoption in Poland is surging, positioning the country as a key player in Europe’s digital asset economy. Chainalysis’s 2025 Europe Crypto Adoption report ranks Poland eighth in the region for total cryptocurrency value received between July 2024 and June 2025, with over 50% year-over-year growth in transaction volumes. This expansion highlights resilient user interest, driven by increasing awareness and accessibility of crypto platforms.
Polish investors are particularly drawn to Bitcoin, evidenced by the proliferation of Bitcoin ATMs. As of January 2025, Poland hosts the world’s fifth-largest network of these machines, outpacing even El Salvador, a nation that has integrated Bitcoin into its financial system. This infrastructure boom facilitates easier entry for retail users, with installations rising by 40% in the past year alone, according to industry trackers. The regulatory vacuum, while challenging, has not dampened enthusiasm; instead, it has encouraged peer-to-peer transactions and decentralized finance activities.
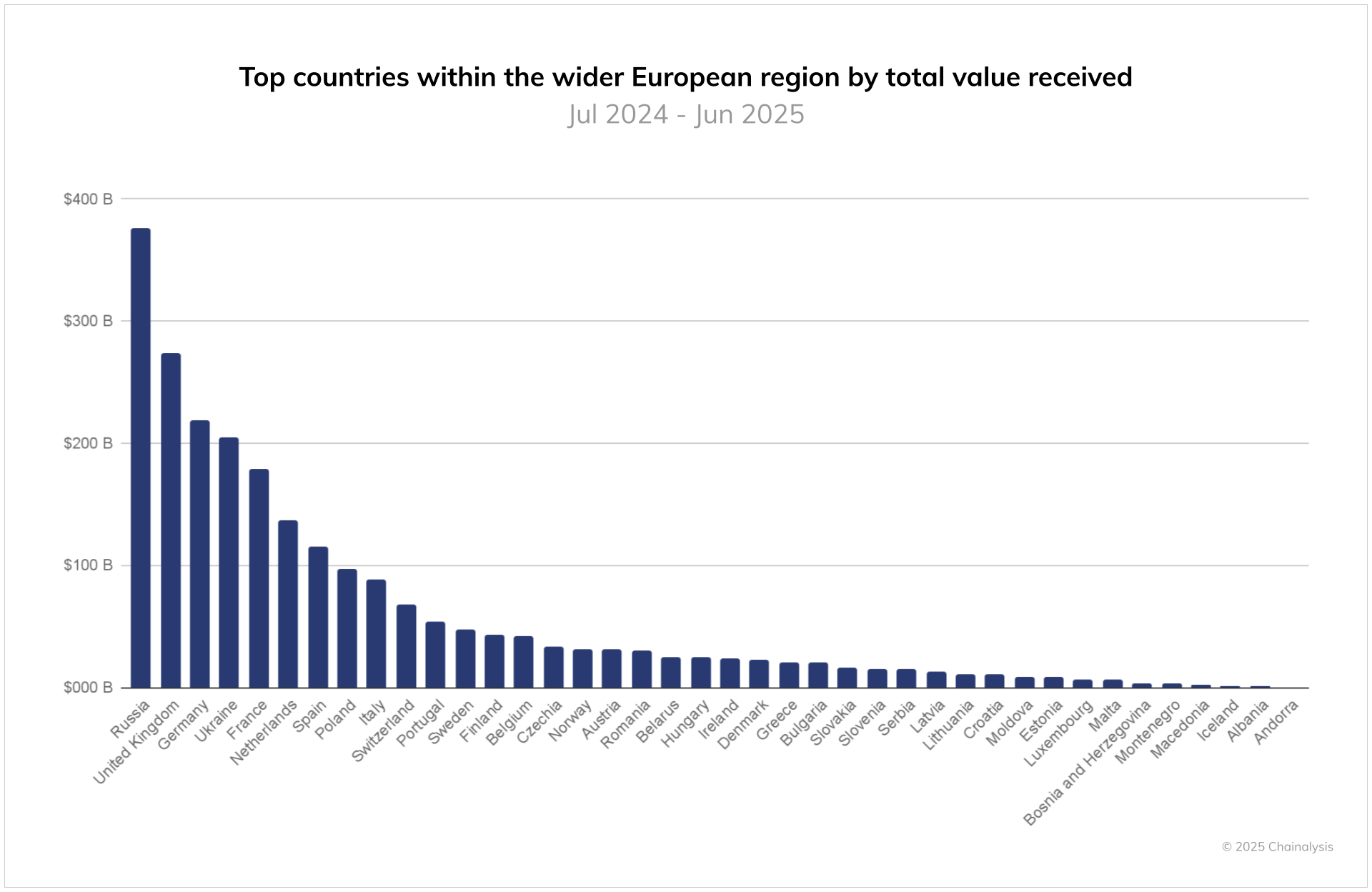
Poland ranked eighth in Europe in terms of total cryptocurrency value received between July 2024 and June 2025. Source: Chainalysis
The crypto industry’s opposition to the vetoed bill stems from fears that heavy-handed rules would stifle this momentum. Groups representing startups have advocated for a more balanced approach, emphasizing the need for innovation-friendly policies. Chainalysis data further illustrates this trend, showing Poland’s on-chain activity expanding significantly, with DeFi protocols seeing a 60% increase in user engagement. As one anonymous industry executive remarked to Bloomberg, “Regulation is necessary, but it must evolve with the technology to avoid choking off Poland’s potential as a crypto hub.”
Looking ahead, the delay in enacting the Crypto-Asset Market Act could influence how Poland integrates with the broader EU framework. MiCA, fully implemented across most member states, provides a template for stablecoin oversight and asset classification, but Poland’s unique political dynamics add complexity. Financial analysts predict that without swift legislative action, the country risks lagging behind neighbors like Germany and France in attracting institutional investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main reasons for the veto of Poland’s Crypto-Asset Market Act?
The veto by President Karol Nawrocki was primarily due to concerns over threats to personal freedoms, property rights, and state stability posed by the bill’s strict provisions. It included heavy compliance burdens and criminal liabilities that critics argued would harm innovation. This decision, upheld by parliament, requires the government to redraft the legislation for better balance.
How will the Crypto-Asset Market Act veto affect crypto users in Poland?
For everyday crypto users in Poland, the veto means continued regulatory uncertainty, potentially delaying protections against fraud while allowing current adoption trends to persist unchecked. It buys time for more tailored rules, but users should remain vigilant about security in the absence of formal oversight, much like navigating the open financial waters of decentralized markets.
Key Takeaways
- Regulatory Delay: Poland’s failure to override the veto stalls EU-aligned crypto rules, prolonging uncertainty for the sector.
- Growing Adoption: Despite hurdles, transaction volumes rose over 50% year-over-year, per Chainalysis, underscoring strong market interest.
- Balancing Act: Future laws must weigh security needs against innovation to keep Poland competitive in Europe’s crypto landscape.
Conclusion
The upholding of President Nawrocki’s veto on Poland’s Crypto-Asset Market Act marks a pivotal moment in the nation’s approach to crypto regulation, highlighting deep divisions between security imperatives and the drive for innovation. As crypto adoption in Poland continues to accelerate, with robust growth in transactions and infrastructure, the government faces pressure to craft a forward-thinking framework aligned with EU standards like MiCA. Stakeholders should monitor upcoming legislative efforts closely, as balanced Poland crypto regulation could unlock substantial economic opportunities in the years ahead.
Comments
Other Articles
Bitcoin Price Analysis: Will the Uptrend Continue?
2/28/2026
Ethereum 2.0 Update: How Will It Affect the Crypto Market?
2/27/2026
The Coming of Altcoin Season: Which Coins Will Stand Out?
2/26/2026
DeFi Protocols and Yield Farming Strategies
2/25/2026
