Upbit Hacker May Use Railgun to Mix Stolen Solana Assets
SOL/USDT
$4,203,361,175.30
$82.37 / $77.12
Change: $5.25 (6.81%)
-0.0056%
Shorts pay
Contents
The Upbit hacker laundered stolen funds through the Railgun privacy mixer, evading its zero-knowledge checks due to outdated wallet data. This multi-chain exploit, involving over $36 million primarily in Solana assets, highlights vulnerabilities in mixer protocols and exchange security.
-
Upbit Hack Overview: A sophisticated attack stole more than $36 million, focusing on Solana-based tokens swapped rapidly across chains.
-
Railgun Mixer Role: The privacy tool allowed fund mixing despite checks, as hacker wallets were not yet flagged in its database.
-
Impact and Response: On-chain analysis by experts like @dethective revealed patterns linked to state-sponsored actors, with Upbit patching internal flaws.
Discover how the Upbit hack exploited Railgun mixer for laundering $36M in crypto. Learn key details, security lessons, and privacy tool risks in this in-depth analysis. Stay informed on blockchain threats today.
What is the Connection Between the Upbit Hack and the Railgun Mixer?
The Upbit hack and Railgun mixer are linked through the hacker’s use of Railgun to obscure stolen funds following a major breach at the South Korean exchange. In the incident, attackers siphoned over $36 million, predominantly Solana assets, through a flaw in Upbit’s internal system involving predictable key hashing. The funds were quickly swapped and bridged, eventually mixed via Railgun’s zero-knowledge proofs, which failed to flag the illicit origins due to rapidly evolving wallet addresses.
How Did the Hacker Evade Railgun’s Security Checks?
The Railgun protocol employs zero-knowledge proofs to verify the legitimacy of funds without revealing transaction details, drawing from databases updated with known illicit addresses. However, in the Upbit case, the hacker’s operations outpaced these updates; on-chain investigations revealed that addresses tied to the breach underwent multiple decentralized exchange swaps, creating fresh wallets hours after the attack. For instance, the last intercepted wallet processed 410 ETH, but a new intermediary address slipped through because Railgun’s data lagged behind the exploit’s speed. Experts from blockchain analytics firms, such as those cited in reports from PeckShield, emphasize that such rapid wallet rotations exploit the time gap in mixer blacklists. This incident underscores the limitations of current privacy tools, where even robust checks like Railgun’s can be bypassed by agile adversaries. According to statements from Upbit’s security team, the initial breach stemmed from weak cryptography in hot wallet management, allowing private key inference from public data—a vulnerability now patched to prevent recurrence. Broader statistics from Chainalysis indicate that over 70% of illicit crypto flows in 2025 involve mixers, highlighting the ongoing cat-and-mouse game between hackers and compliance mechanisms. Railgun’s growth, with $95 million in total value locked as of late 2025 and $1.31 million in Q3 fees, reflects rising demand for privacy amid regulatory scrutiny, yet it also attracts scrutiny when tied to exploits like this one.
The Upbit hacker may be using Railgun to mix funds. Despite the mixer’s checks, the hacker addresses were not flagged, and the transactions were allowed to continue.
On-chain analysis showed addresses linked to the Upbit hack used the Railgun mixer. The mixer performs a zero-knowledge check for the origin of funds. This time, however, the check did not prevent the funds from being mixed.
Upbit was hacked for over $36M, with over $30M in Solana assets. The multi-chain attack led to immediate swaps and movements of funds between wallets.
The hacker sold most assets almost immediately, especially Solana-based tokens. On-chain investigator @dethective noted the selling had an effect on decentralized market volumes. The day after the hack, the exploiter’s wallets swapped Solana tokens into SOL. After that, the SOL was traded for USDC, and the stablecoins were bridged to Ethereum for mixing.
In total, the hacker held over 533 ETH after fees, valued at around $1.6M. The shift to Ethereum and subsequent mixing is a pattern usually ascribed to North Korean hackers.
Upbit also added new information on its hack. According to a statement from the exchange, the exploit may be due to a flaw in the exchange’s internal system, which has been patched. Upbit stated that the hacker may have inferred private keys from publicly available hot wallets due to predictable key hashing and weak cryptography.
Railgun lacked the latest information on the hackers’ wallets
Railgun’s approach is to test each user’s wallets against constantly updated databases for bad actors. In this case, the hacker’s full list of addresses was very recent. Additionally, the exploit went through multiple direct DEX swaps and some of the funds were shifted to new wallets. The data available to Railgun was therefore outdated, and the hacker’s latest wallet passed the test.
The last intercepted wallet laundered a total of 410 ETH. The new address was created just hours after the hack, and briefly used as an intermediary. The rapid change in wallets additionally avoided Railgun’s filters.
Railgun used for DeFi activity
Railgun gained popularity during the recent revival of the privacy narrative. Railgun grew its asset pool, with $95M in value locked as of November 2025. The increased value signals a growing interest, as the mixer achieved $1.31M in fees for Q3.
The usage of mixers grew in the past year. Tornado Cash, previously seeing only baseline activity, increased its value locked to a new peak. The mixer holds over 32K ETH, following multiple high-profile exploits.
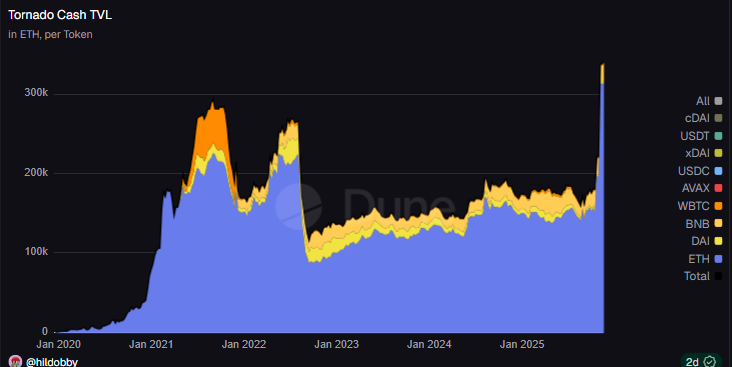 Tornado Cash posted a record number of ETH in its reserves after an increased demand for privacy. | Source: Dune Analytics
Tornado Cash posted a record number of ETH in its reserves after an increased demand for privacy. | Source: Dune AnalyticsThe native RAIL token also rose by over 200% for the past three months, trading at $3.26. Railgun reflected the success of ZCash and other privacy tokens, while also being promoted by Vitalik Buterin.
Railgun is not a go-to tool for hackers and exploiters. Rather, it has been a general privacy tool for regular transactions. Crypto influencers and high-profile individuals aim for privacy, as even transaction data can lead to tracking or even price swings.
However, Railgun usage can also be tracked. Additionally, hacker addresses can use tools to test which wallets would be flagged by Railgun. This would allow hackers to keep hiding the proceeds of exploits, most of which are untraceable.
Delving deeper into the mechanics, the Upbit breach exemplifies how centralized exchanges remain prime targets for sophisticated actors. The attack’s multi-chain nature—starting with Solana exploits and bridging to Ethereum—demonstrates the hacker’s technical prowess. Post-hack, the rapid liquidation of assets depressed trading volumes on affected decentralized platforms, as noted by on-chain sleuths. Upbit’s disclosure of the vulnerability, involving flawed hashing algorithms, aligns with broader industry warnings from cybersecurity firms like Certik, which report a 25% uptick in key-derivation attacks in 2025. The Ethereum bridging phase, culminating in 533 ETH holdings worth $1.6 million, mirrors tactics observed in Lazarus Group operations, per U.S. Treasury attributions. Railgun’s protocol, built on zk-SNARKs for shielding transactions, prioritizes user privacy but relies on collaborative threat intelligence feeds that can lag during fast-moving incidents. This event has prompted discussions in the DeFi community about enhancing real-time oracle integrations for mixers, ensuring databases reflect exploits within minutes rather than hours.
Furthermore, the surge in mixer adoption ties into the evolving regulatory landscape. With entities like the EU’s MiCA framework mandating transaction transparency, tools like Railgun offer a compliant privacy layer for legitimate users. Yet, the Upbit case illustrates the dual-use dilemma: privacy innovations inadvertently aid illicit flows. Data from Elliptic shows that while 90% of mixer volume stems from non-malicious activity, high-profile hacks amplify perceptions of risk. Upbit’s swift patching and user compensation efforts—reimbursing affected accounts—bolster its reputation, but the incident serves as a cautionary tale for exchanges worldwide to audit cryptographic implementations rigorously.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Caused the Upbit Hack Involving Railgun Mixer Laundering?
The Upbit hack stemmed from a vulnerability in the exchange’s hot wallet system, where predictable key hashing allowed attackers to infer private keys from public data. Over $36 million in assets, mainly Solana tokens, were stolen and laundered through Railgun, which failed to flag the funds due to outdated blacklists. Upbit has since patched the flaw and enhanced security protocols.
How Can Users Protect Themselves from Similar Crypto Hacks and Mixer Risks?
To safeguard against hacks like Upbit’s and mixer-related laundering, users should enable two-factor authentication, use hardware wallets for significant holdings, and monitor on-chain activity via tools like Etherscan. For privacy needs, opt for audited mixers with strong compliance features, and always diversify assets across reputable exchanges with proven track records.
Key Takeaways
- Rapid Wallet Rotation Evades Detection: Hackers can bypass mixer checks by creating new addresses quickly after exploits, as seen in the Upbit Railgun incident.
- Exchange Vulnerabilities Persist: Weak cryptography in hot wallets remains a common entry point; regular audits and patches are essential for platforms like Upbit.
- Privacy Tools Demand Balance: While Railgun aids legitimate privacy, integrating faster threat updates can mitigate misuse without compromising user anonymity—consider advocating for such improvements in the crypto ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Upbit hack and Railgun mixer saga reveal critical intersections of exchange security flaws and privacy protocol limitations in the crypto landscape. With over $36 million laundered through evasive tactics, this event emphasizes the need for real-time blockchain monitoring and robust cryptographic standards. As mixers like Railgun continue to grow amid privacy demands, exchanges must prioritize vulnerability assessments to protect users. Looking ahead, enhanced collaboration between platforms and analytics providers will fortify defenses—stay vigilant and explore secure DeFi practices to navigate these evolving threats effectively.
